
Phishing is a classic form of cyber fraud in which attackers often impersonate trusted institutions or individuals to trick victims into revealing sensitive information. Although this type of fraud has been around for decades, it remains one of the most common and effective methods for penetrating companies, stealing data, and conducting financial fraud. Its success lies in the use of social engineering, manipulating human trust, emotions, and impulses to lead the target to make poor decisions.

Phishing attacks are typically carried out via email, fake websites, applications, phone calls, text messages, and social media. These attacks exploit human weaknesses (such as impulsiveness, curiosity, and trust) to lure victims into providing personal information, clicking on malicious links, downloading malware, or transferring funds.
As AI becomes more widespread, phishing strategies continue to evolve, and fraud techniques become more complex and covert.** Fraudsters can use AI to generate realistic and customized phishing content, significantly increasing the deception and success rate of their attacks. According to 2023 data, AI-driven phishing scams have surged by 3,000%, demonstrating the immense threat of this new technology.
Changes AI Brings to Phishing Attacks
-
Making Phishing Attacks Easier: AI dramatically lowers the threshold for phishing attacks, especially in cross-language attacks. Traditional phishing requires attackers to have a certain level of language proficiency, while AIGC can generate high-quality text, voice, and images based on simple prompts and automatically correct spelling and grammatical errors. This means that attackers can generate seamless phishing content in multiple languages, making it easy to target victims across different regions of the world.
-
Making Phishing Emails More Convincing: AI can quickly collect, analyze, and integrate publicly available information about an organization or individual, such as social media profiles, news reports, or other public data. Based on this data, AIGC can generate customized “bait files,” making phishing emails more credible and realistic. As AI-generated content is highly intelligent, the typical red flags in phishing emails, such as grammatical errors, spelling issues, or improper formatting, are entirely eliminated, making it difficult for victims to detect.
-
Diversifying Phishing Methods: AI can generate not only precise text but also personalized voice and video content. This allows phishing attacks to expand from traditional emails to voice phishing (vishing) and video phishing (deepfakes). Attackers can create simulated phone voices, fake video conferences, or social media interactions, mimicking real voices and images to deceive targets. This diversity in attack methods makes phishing no longer confined to a single text-based channel but more three-dimensional and multi-layered.
-
Making Phishing Attacks Harder to Detect: Egress’s 2023 phishing threat trend report shows that in three-quarters of cases, traditional security measures struggle to distinguish AI-generated phishing emails from those written by humans. This is because AI-generated content is highly natural and intelligent, avoiding the typical crude traces found in phishing attacks. Security technologies and systems need further development to meet this challenge, as existing anti-phishing tools are increasingly struggling to detect and defend against such advanced attacks effectively.
-
Making Phishing Attacks More Targeted: AI can help attackers create highly personalized attacks by tailoring content based on the target's interests, habits, profession, and social network. By analyzing social networks, public profiles, and other digital footprints, AI can simulate the target's life scenarios, professional environment, and even daily conversation styles to carry out highly precise, targeted attacks. Compared to traditional broad-scope attacks, AI-driven phishing attacks have a significantly higher success rate and destructive power, as their content better aligns with the target's expectations and trust patterns.
AI Diversifies Phishing Methods
-
Phishing Email: Email phishing is the most common form of phishing, often impersonating official emails from well-known financial institutions, government departments, or other legitimate organizations. Attackers typically ask recipients to provide login credentials, bank account information, or click on malicious links to download malware or trojans. The design of the emails often mimics real email templates, even including legitimate companies' logos, contact information, and other visual elements to increase credibility.

-
Website Phishing: Website phishing typically involves creating fake websites almost identical to legitimate ones, with URLs differing by only a single character, making them extremely difficult to distinguish. Users are often tricked into entering personal information, credit card data, or login credentials on these counterfeit websites. Attackers may even use SSL certificates (https) to increase the credibility of their fake websites, deceiving victims into believing they are interacting with a legitimate site.
-
Smishing: Attackers send fake text messages pretending to be from banks, government agencies, or other trusted organizations, which contain links to malicious websites or induce victims to call scam numbers. Smishing usually employs urgent or tempting content, such as frozen bank accounts or unexpected winnings, to provoke a quick response from users, causing them to overlook careful scrutiny of the link or message.
-
Vishing: Voice phishing involves attackers directly calling targets or using automated voice messages to scam them. Attackers impersonate bank representatives, law enforcement, or tech support, attempting to obtain sensitive information such as bank account details, passwords, or social security numbers through voice communication. Vishing often emphasizes urgency and authority, trying to pressure victims into disclosing information.
-
Social Media Phishing: On social media platforms, phishing typically appears as enticing offers, free gifts, or breaking news. Attackers use fake accounts and malicious links to lure users into clicking, leading to the installation of malware or the disclosure of information. Attackers may also use social engineering techniques to impersonate the user's friends or colleagues, further increasing the success rate of the attack.
-
QR Code Phishing: With the rise of QR codes, malicious QR phishing has become a new attack method. Attackers may distribute malicious QR codes via emails, flyers, or public spaces, luring users to scan and access malicious websites or download malicious applications. Since QR codes do not directly display URLs, users may unknowingly fall into a trap after scanning them.
How to Prevent AI Phishing Fraud
The intelligence bulletin "DEEPFAKE Threat Research and Security Strategies" suggests that to prevent and combat AI fraud, it is essential to both effectively detect and identify AI-generated content and to prevent the exploitation and spread of AI fraud. This requires not only technical solutions but also sophisticated psychological strategies and the enhancement of public safety awareness.
-
Comparison and Identification of Device Information, Geographical Location, and Behavioral Operations. Dingxiang Device Fingerprinting can help identify legitimate users and potential fraudulent behaviors through the recording and comparison of Device Fingerprinting. This technology uniquely identifies and recognizes each device, detecting maliciously controlled devices such as virtual machines, proxy servers, and emulators. It analyzes whether the device shows abnormal behaviors or actions that do not align with the user’s habits, such as logging into multiple accounts, frequently changing IP addresses, or frequently modifying device attributes, thus helping track and identify fraudsters' activities.
-
Detection of Account Anomalies. Strengthen frequent authentication in cases of abnormal activities such as account login from different locations, device changes, phone number changes, or sudden activity in dormant accounts. Continuous identity verification during sessions is crucial; persistent checks should be conducted to ensure that the user's identity remains consistent throughout usage. Dingxiang atbCAPTCHA can quickly and accurately differentiate between human and machine operators, accurately identifying fraudulent actions and providing real-time monitoring and interception of abnormal behavior.
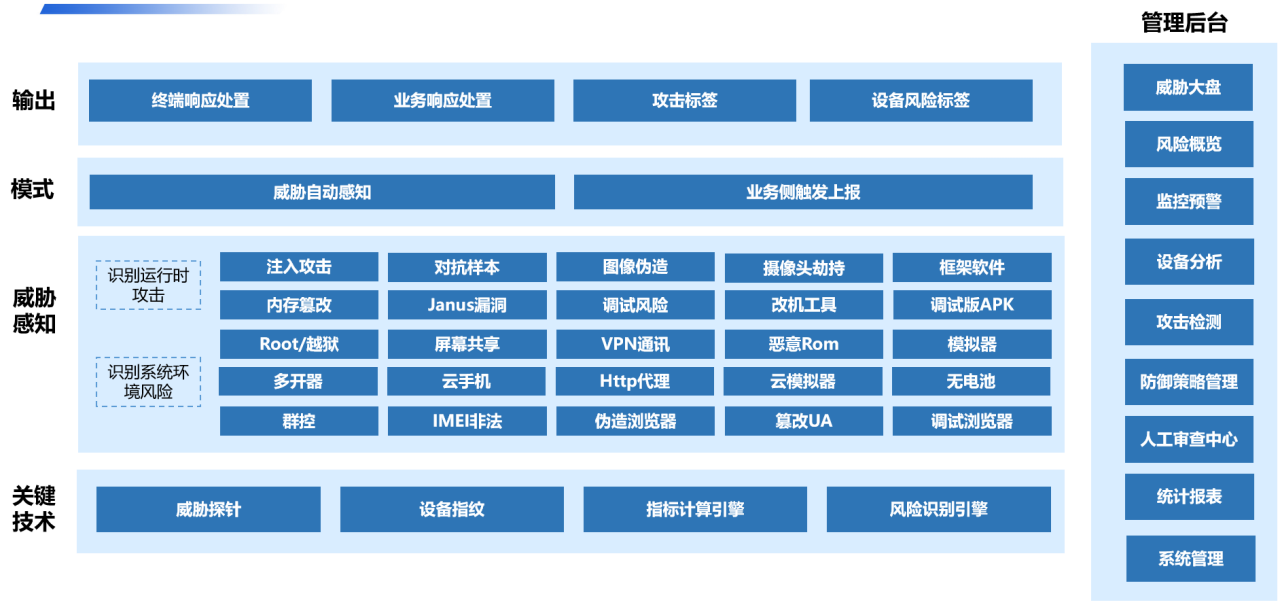
-
Prevention of Fake Videos and Images. Dingxiang's Full-Chain Panorama Facial Security Threat Perception Solution uses intelligent verification through multidimensional information such as device environment, facial information, image forgery detection, user behavior, and interaction status. It rapidly identifies more than 30 types of malicious attacks, including injection attacks, liveness forgeries, image forgeries, camera hijacking, debugging risks, memory tampering, rooting/jailbreaking, malicious ROMs, emulators, and other system or operational threats. Upon detecting forged videos, fake facial images, or abnormal interaction behavior, it can automatically block operations. The solution also allows flexible configuration of video verification intensity and user-friendliness, implementing a dynamic mechanism to use atbCAPTCHA for regular users and strengthen verification for suspicious users.
-
Uncovering Potential Fraud Threats. Dingxiang Dinsight's Real-Time Risk Control Engine helps companies assess risks, analyze fraud, and conduct real-time monitoring, improving the efficiency and accuracy of risk management. The average processing speed of Dinsight’s daily risk control strategy is within 100 milliseconds, supporting the integration and storage of multi-party data. Based on mature indicators, strategies, and experience in modeling, coupled with deep learning technology, Dinsight implements a self-monitoring and self-iterating mechanism for risk control performance. Together with Xintell Intelligent Model Platform, it enables automatic optimization of security strategies for known risks and supports risk control strategies across different scenarios with one-click configuration. Xintell standardizes complex data processing, mining, and machine learning processes, providing an end-to-end modeling service from data processing, feature derivation, model building, to final model deployment.


