
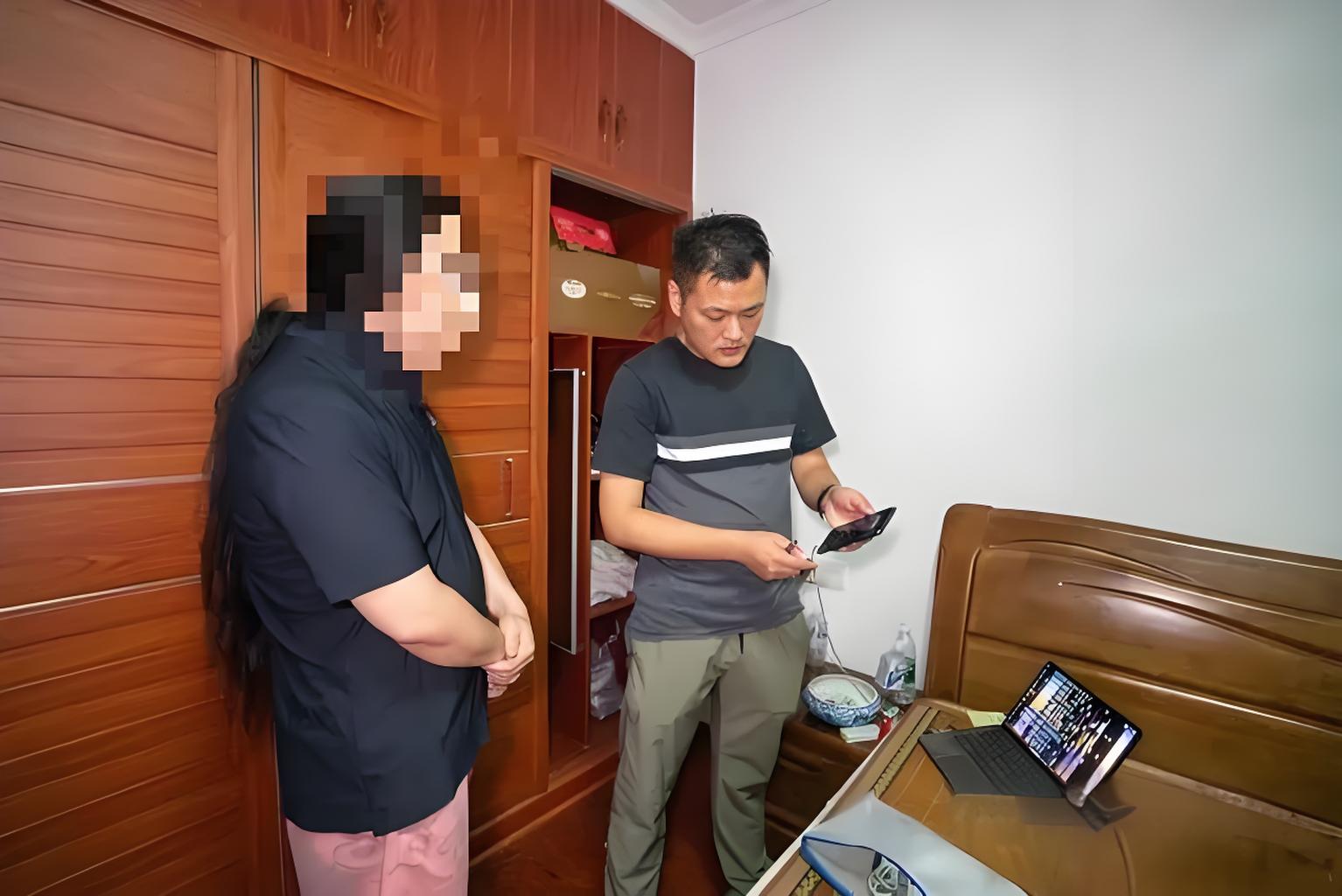
Recently, the Nanjing police launched a comprehensive crackdown on ticket scalping around the Nanjing Museum, successfully arresting 67 suspects and uncovering two criminal gangs that illegally used technological means to seize and resell tickets for cultural and tourist venues.
The Nanjing Museum has a reception limit of 22,000 visitors per day, but the number of reservations often exceeds one million. Due to the scarcity of tickets, scalpers have been reselling free tickets at inflated prices. In addition to the Nanjing Museum, this also involves the National Museum, the Great Hall of the People, the Shanghai Science and Technology Museum, and more than a dozen other scenic spots. Tourists have reported that on some idle social platforms, anonymous users resell Nanjing Museum tickets, either by directly inflating the prices or bundling them with "guides" to sell them at inflated prices of up to 100-200 yuan. Behind the "hard-to-get" tickets, a gray industry chain has quietly taken shape on the internet, with clear division of labor.
The police investigation found that multiple criminal gangs were behind the ticket scalping, and the division of labor within these gangs enabled rapid expansion, forming a stable profit chain.
For example, one suspect developed "ticket-snatching software" for the Nanjing Museum and other popular cultural and tourist venues, specifically designed to quickly grab tickets. Another suspect was responsible for posting information on social media and various platforms to attract large-scale "ticket scalpers" and find target customers. Once the tickets were sold, the two split the earnings according to a set ratio. Within just over a month, the two earned nearly 300,000 yuan.
The gang's illegal actions seriously undermined the fairness of the online reservation system for the Nanjing Museum and other cultural and tourist venues, constituting the crime of damaging computer information systems. The police have taken criminal measures against all the suspects involved to maintain market order.
Analysis of the "Ticket-Snatching Software" Used by Scalpers
The criminal gang's "ticket-snatching software" operates with a high level of automation, completing the entire ticket purchase process in just a few seconds.

High-Frequency Access: The software uses multiple IP addresses from different areas in Guizhou to make high-frequency requests, sending a large number of requests in a short period, creating an abnormal situation that human operators cannot achieve.
Millisecond-Level Request Intervals: The time intervals between requests are compressed to milliseconds, with the system receiving more than 2,000 visits per day. This behavior can be metaphorically compared to "thousands of people with the same face and clothes, bypassing the community security gate, and standing at your door, coming thousands of times a day."
Speed is crucial in ticket-snatching. If person A is one second faster than person B, A will be able to purchase the ticket while B will not. In terms of speed, humans rely on their neurological reactions, but software operates based on pre-set processes, making it much faster than humans, significantly increasing the success rate of ticket purchases.
Preventing Scalpers from Using Software to Snatch Tickets
Although many museums have implemented ticketing rules and technical measures to regulate scalpers, such as blocking frequent reservations from specific phone numbers or IP addresses, scalpers continue to develop new cheating tools. These ticket-snatching tools can perform batch registration, login, and ticket grabbing operations, enabling them to quickly and automatically seize designated tickets in an instant. By filling in personal information, setting the quantity, and scheduling the running time, they can complete the automatic purchase process.
Therefore, simply limiting IP addresses is not enough and may inadvertently block legitimate visitors' reservations. Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center recommends that, in addition to restricting IP addresses and accounts, more technical measures should be implemented to prevent scalpers from using cheating software to effectively curb the reselling of tickets.
Ticketing Rule Restrictions
-
Increase the usage limit of identification documents. Each identification number can only make one reservation; each account can reserve tickets for up to 5 people.
-
Increase account usage limits. Some museums require that if an account makes multiple reservations within a week and has a no-show rate exceeding 50%, that account (or phone number) will be restricted from making reservations for 30 days. Some museums also require that if an account cancels reservations more than three times within 7 days or five times within 30 days, or fails to enter the venue after making a reservation, the account will be locked in a "blacklist" for 30 days and cannot make any reservations, to prevent scalpers from repeatedly using identity information they control.
-
Increase ticket sale times and channels. Irregular ticket releases and the addition of manually issued random tickets can help reduce the occurrence of technical ticket-snatching to some extent.
Technical Measures for Prevention
- Detect and identify abnormal devices. Identify whether the client’s Device Fingerprinting is legitimate, and check for risks such as injection, hooks, emulators, and more. Quickly identify risks related to flashing, rooting, jailbreaking, hijacking injections, and abnormal behaviors such as multiple activations on the same device, abnormal IP associations from the same device, abnormal behavior patterns in older device models, and abnormal use of old operating systems within the same channel.
Dingxiang Device Fingerprinting can detect virtual machines, proxy servers, emulators, and devices that are maliciously controlled. It analyzes whether devices exhibit abnormal or unusual behaviors, such as frequent switching of accounts, frequent IP address changes, or frequent changes in device attributes. This helps track and identify fraudulent activities early on and prevent fraudulent claims. It can also serve as an additional identity verification factor, enhancing the security of user logins and transactions. By recording and comparing Device Fingerprints, legitimate users and potential fraudulent activities can be distinguished.
- Detect and intercept abnormal accounts. Based on user behavior, strategies can be deployed to monitor accounts that initiate orders after switching a large number of accounts on the same device.
Dingxiang atbCAPTCHA can perform real-time verification, identification, and interception of malicious accounts and crawling behaviors during key actions like registration, login, and queries. Based on AIGC technology, it can prevent AI-based brute force cracking, automated attacks, and phishing attacks, effectively preventing unauthorized access and blocking web crawlers from stealing data. It integrates 13 verification methods and multiple preventive strategies, supports seamless user experience for legitimate users, and reduces real-time response time to under 60 seconds, further enhancing the convenience and efficiency of login services.
- Enhance risk identification and prevention capabilities. Establish a local dynamic operation and maintenance mechanism for black and white lists based on registration data, login data, and activation data, including user IDs, phone numbers, devices, and other dimensions. After accumulating a certain amount of online data, the risk control data and business accumulation can be used to model behaviors like registration, login, ordering, and ticket-snatching. The model’s output can be directly applied to risk control strategies.
Dingxiang Dinsight helps businesses perform risk assessments, anti-fraud analysis, and real-time monitoring, improving the efficiency and accuracy of risk control. The Dinsight system, along with the Xintell intelligent model platform, can automatically optimize security strategies for known risks, mine potential risks based on logs and data, and configure one-click risk control strategies for different scenarios.
The police remind tourists not to trust false ticketing information regarding "ticket-snatching services" on social media platforms. These services pose risks of personal information leakage and may even lead to scams. If you encounter any suspicious activity, please call 110 to report it and protect your rights.


