
E-commerce shopping festivals are not only a feast for consumers but also a honey pot for black and grey industries. On the one hand, during major events like 618, many e-commerce platforms lower their business security sensitivity and relax some risk control rules to avoid impacting customer experience and ensure stable business operations. On the other hand, black and grey industries employ new fraudulent methods in increasingly covert and sophisticated ways to maximize profits.
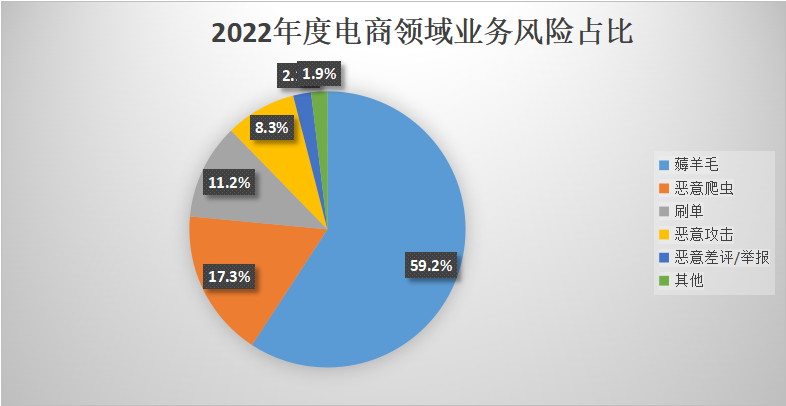
 According to data previously released by Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center, the highest risks occur during shopping events like Double 11 and 618, with November accounting for 39.72% and June for 20.69%.
According to data previously released by Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center, the highest risks occur during shopping events like Double 11 and 618, with November accounting for 39.72% and June for 20.69%.
The marketing cycle for e-commerce platforms spans from half a month to a month before the frenzy day, with marketing investments lasting 1-2 months. This ample time allows black and grey industries to study the processes and rules of various e-commerce platforms in preparation for subsequent fraudulent activities. Popular products and promotions become means for them to profit.
Coupon farming: Popular products taken away by merchants
During shopping festivals, countless consumers eagerly anticipate, yet many discounted or special-priced items often show "sold out" or "temporarily out of stock". What causes this? It turns out that many popular, limited-sale, or high-value products are snapped up by coupon farmers.
Actions like coupon clipping and grabbing flash sale items not only harm the legitimate interests of consumers but also lead to significant economic losses for consumers, merchants, and e-commerce platforms. Data shows that 70%-80% of e-commerce enterprises' marketing expenses are consumed by coupon farmers, resulting in annual losses amounting to hundreds of billions.
Coupon farmers engage in activities such as grabbing coupons, seizing flash sale items, and registering fake users, causing significant economic losses to consumers, merchants, and e-commerce platforms.
Bulk registration of fake accounts. Registration is a key process for creating an account. Black and grey industries utilize registration tools for automated bulk account creation, registering hundreds to tens of thousands of accounts to facilitate mass purchases and hoarding.
Using group control to manipulate accounts. Black and grey industries utilize group control to operate tens, hundreds, or even thousands of devices from a single computer, performing unified actions such as registration, login, ordering, and purchasing. Group control also offers functions like simulated location, shake-to-refresh, bulk contact list import, and message pushing.
Forging IP locations. An IP address represents a user's network information when online. Black and grey industries use tools for rapid IP dialing, automatically calling dynamic IP addresses across regions, with features like automatic switching, reconnecting after disconnection, automatic browser cookie cache clearance, and virtual network card information, seamlessly switching between domestic and international IPs.
Forging GPS locations. GPS positioning indicates a user's geographical location during online service use. Black and grey industries utilize simulation software and third-party tools to change latitude and longitude, enabling instant "teleportation" to any location.
Forging device attributes. Device attributes like model, serial number, and IMEI are unique identifiers. Black and grey industries use device modification tools to intercept device interfaces at the system level. When applications call these interfaces to retrieve device parameters, they receive attributes forged by the modification tool. Typically, it takes 2-3 minutes for such tools to modify attributes for 1000 devices.
# How merchants can prevent coupon farming
Business risk fraud constantly evolves with rapid changes in methods. New attack methods adjust existing preventive measures or render them immune. Traditional measures often fail to timely identify and alert new risks, and contradictions among various e-commerce platform security processes sometimes lead to direct impacts on order transactions and store operations.
Identify and alert risk IP addresses. Integrate an IP risk database to match user-associated IPs for risk identification, identifying risks like proxies and rapid dialing IPs, and intercepting malicious IP addresses.
Identify and alert risk devices. Assess whether client device fingerprinting is legitimate, detecting risks like injection, hooking, and simulation software. Quickly recognize risks associated with rooted devices, jailbroken devices, or devices hijacked for injection. Rapidly identify abnormal behaviors such as repeated activations from the same device, abnormal IP clustering within a short time, unusual proportions of old device models or operating systems within the same channel.
Identify and intercept risky accounts. Analyze verification environment information and tokens during validation completion to promptly detect anomalies and risky operations. Monitor abnormal account behaviors. Deploy strategies based on user behavior, focusing on accounts that frequently switch from the same device during order initiation.
Analyze and forecast future behavioral risk changes. Establish and maintain a dynamic operation mechanism for local lists based on registration, login, and activation data, accumulating and maintaining corresponding black and white list data dimensions such as user ID, phone number, and device. After accumulating online data, use risk control and business accumulation data to model registration, login, ordering, and purchasing behaviors, directly incorporating model outputs into risk control strategies.
Advertising fraud: causing colossal promotional efforts by e-commerce platforms to go down the drain
During online shopping festivals, e-commerce platforms heavily invest in advertising and native advertising to attract more consumers. Unscrupulous individuals exploit various methods such as ad clicking and falsifying promotional data to reap benefits. On one hand, after advertising campaigns, stakeholders only see corresponding click-through rates, activation rates, and registration rates, with very low retention rates. On the other hand, the data includes a large amount of fake traffic with no conversions from real users, and efforts to analyze failed conversions further cannot pinpoint the true reasons. This not only wastes advertising costs, time, and development expenses but also causes substantial asset losses and a plethora of valueless fake users for advertisers.
Analysis by Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center indicates that perpetrators engage in e-commerce advertising fraud mainly through three forms: manual brushing, machine brushing, and wall brushing.
Manual brushing involves using real devices to manipulate key parameters like IMEI, phone numbers, IMSI, MAC addresses, etc., under human operation, to simulate multiple user downloads, activations, registrations, and usage behaviors for cheating traffic.
Machine brushing entails attackers using a large number of phones to repeatedly change their configurations, masquerading as new devices to repetitively "install-activate-delete-install-activate-delete," thereby inflating activation figures. These devices typically exhibit root access, emulator use, VPNs, abnormal charging states, GPS information, and SIM card behaviors, which can be detected and mitigated by combining device information, tracking user behavior, retention rates, and online durations.
Wall brushing involves genuine human and device operations where users on such platforms are real smartphone users. Although many users uninstall the app after completing tasks, there remains a certain conversion rate. Therefore, many advertisers still opt for wall brushing as a promotional method.
Because of actual rewards, users will go to great lengths to earn rewards through wall brushing, fostering fraudulent behaviors to exploit promotion fees. Some users manipulate batches of fake accounts to complete tasks fraudulently, resulting in heavily adulterated promotional trial data and causing significant losses to advertisers.
How e-commerce platforms can prevent advertising fraud
Based on various advertising fraud methods, Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center recommends that advertisers reinforce terminal protection while leveraging business-side combinations to further safeguard promotional effectiveness.
Ensure client-side security to prevent hijacking by black and grey industries. Dingxiang's adaptive App shielding employs graph neural network technology to analyze and extract code characteristics, automatically selecting suitable methods for obfuscation based on different code blocks to significantly increase the difficulty of reverse engineering, effectively reducing computational performance consumption by 50%. Through encryption and obfuscation engines, it enhances App code security, effectively preventing attacks such as cracking, duplication, and repackaging.
Secure account safety to prevent account theft. Dingxiang's atbCAPTCHA, utilizing AIGC technology, prevents AI-based brute force, automation attacks, and phishing threats, ensuring unauthorized access prevention, account protection from theft, and malicious operations to maintain system stability. It integrates 13 verification methods and multiple prevention strategies, encompassing 4380 risk policies, 112 risk intelligence categories, covering 24 industries and 118 risk types. Its precision in risk control reaches 99.9%, with rapid transformation from risk to intelligence. It supports seamless security verification for users while achieving response times within 60 seconds, further enhancing user login service experience convenience and efficiency.
Identify forged devices to prevent various malicious abnormal behaviors. Dingxiang's Device Fingerprinting integrates multiple device information to generate unified and unique Device Fingerprints for each device. It builds multi-dimensional identification strategy models based on devices, environments, and behaviors to recognize risks like virtual machines, proxy servers, and emulators manipulated maliciously. It analyzes device behavior anomalies such as multiple account logins, frequent IP address changes, and abnormal device attribute changes that do not match user habits, tracking and identifying fraudulent activities to assist enterprises in managing operations under the same ID across all scenarios and channels, enhancing cross-channel risk identification and management capabilities.
Uncover potential fraud threats to prevent various new fraud attacks. Dingxiang's Dinsight aids enterprises in risk assessment, anti-fraud analysis, and real-time monitoring to enhance risk control efficiency and accuracy. Dinsight processes daily risk control strategy with an average speed of less than 100 milliseconds, supporting configurable access and sedimentation of multi-source data. It uses mature metrics, strategies, and deep learning technology to automatically optimize security strategies against known risks, configuring anti-fraud strategies based on risk logs and data mining potential risks. Its standardized data processing, feature derivation, model building, and one-stop modeling service from data processing to final model deployment enhance overall security measures effectively.


