
Recently, a video posted by an account named “Ban Hua XXX” showed a well-known doctor, Zhang Wenhong, promoting a protein bar. However, media investigations revealed that while the lip movements and voice in the video resembled Zhang Wenhong’s, the promotion was not done by him. The video was confirmed to be a deepfake, created using AI technology. Screenshots from users indicated that 1,266 units of the protein bar had been sold. Zhang Wenhong later told the media that there were multiple such fraudulent accounts, which frequently changed, making it challenging to report them.
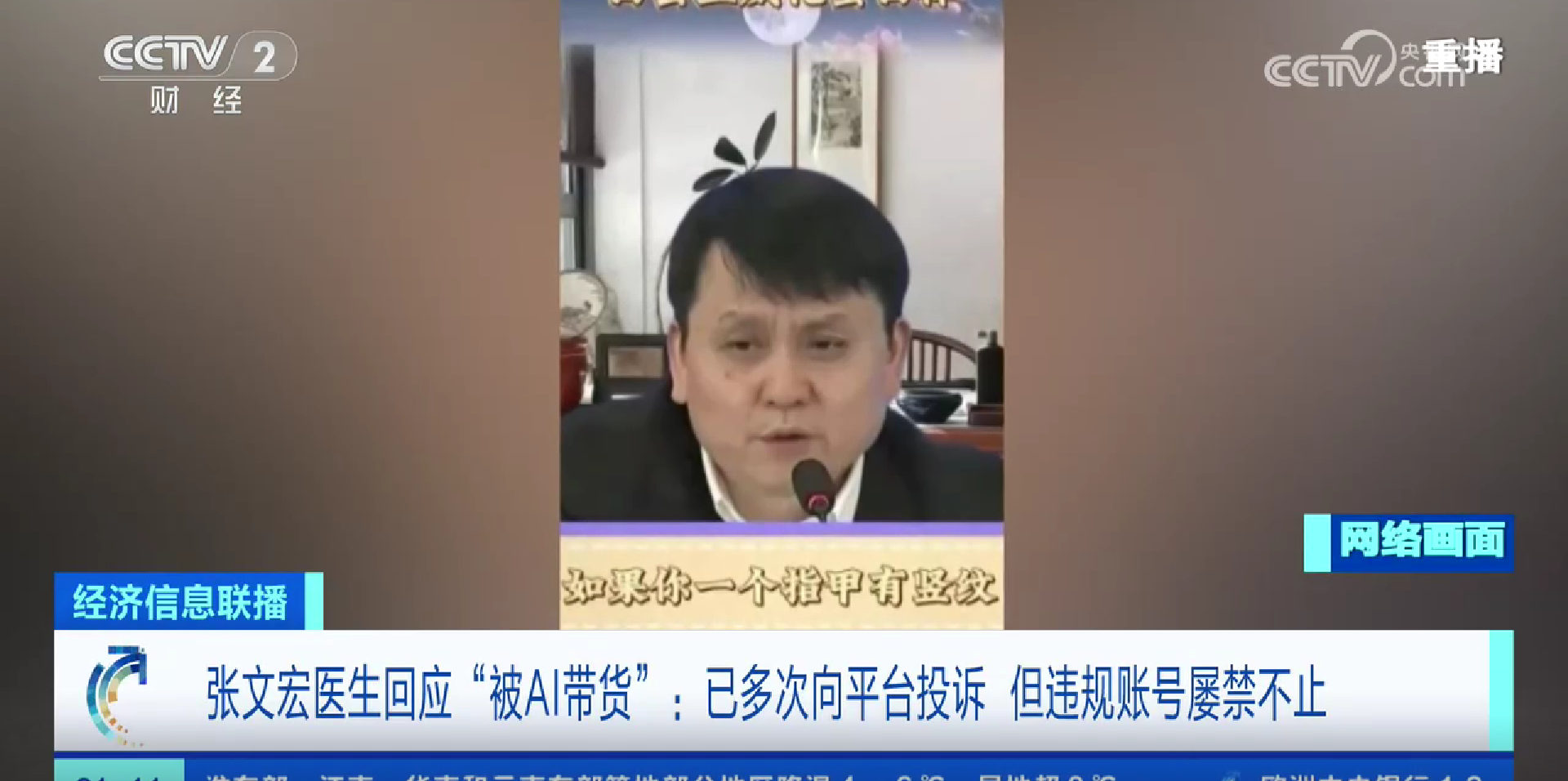
Zhang Wenhong said, “I’ve considered reporting this to the police, but it’s hard to describe an invisible and intangible perpetrator who changes accounts daily and uses only virtual tools. Who can I report? I think this is a violation of consumer rights and should be handled by the relevant authorities.”
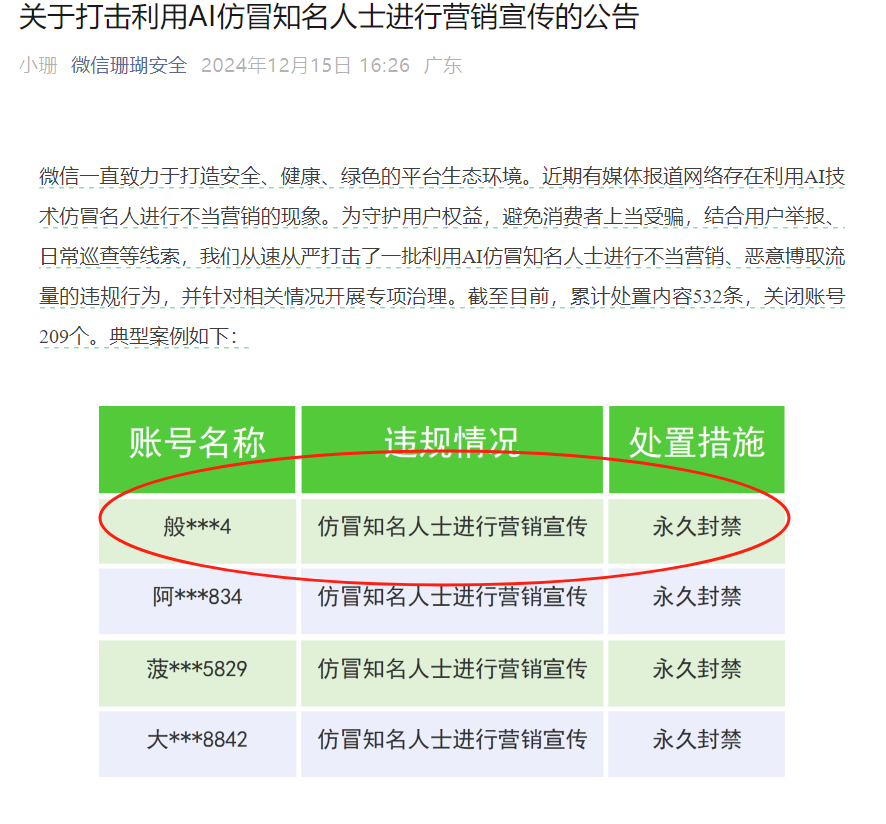 On December 15, the WeChat platform released a statement: “Recently, media reports have highlighted cases of improper marketing using AI-generated impersonations of celebrities. We have taken swift and strict action against accounts that use AI to impersonate well-known individuals for malicious marketing or to gain traffic improperly, and we have launched a special crackdown campaign. So far, 532 pieces of content have been removed, and 209 accounts have been closed. Moving forward, we will increase our efforts to combat violations related to ‘using AI to impersonate public figures for marketing purposes.’”
On December 15, the WeChat platform released a statement: “Recently, media reports have highlighted cases of improper marketing using AI-generated impersonations of celebrities. We have taken swift and strict action against accounts that use AI to impersonate well-known individuals for malicious marketing or to gain traffic improperly, and we have launched a special crackdown campaign. So far, 532 pieces of content have been removed, and 209 accounts have been closed. Moving forward, we will increase our efforts to combat violations related to ‘using AI to impersonate public figures for marketing purposes.’”
How Did Scammers Create Fake Videos of Dr. Zhang Wenhong?
AI-based deepfake technology enables the creation of highly convincing fake images or videos. AI voice cloning can also mimic a target’s voice with high accuracy. These AIGC (AI-Generated Content) fraud techniques have become significant risks in daily life, threatening public safety. Using “deepfake” and “voice cloning” technology, scammers can impersonate celebrities, family members, company executives, or government officials, conducting telecom scams that result in substantial financial losses for victims.

The Financial AIGC Audio and Video Anti-Fraud White Paper, published by the Bank of Communications and Dingxiang, outlines the attack process of deepfake and voice cloning fraud.
AIGC “Deepfake” Attacks
- Fraudsters obtain high-resolution ID photos of victims through purchased identity information.
- These photos are modified using tools like Photoshop to include background elements.
- AI tools are then used to animate the photos, creating fake videos of blinking or head movements.
- These fake videos are injected into apps to bypass identity verification systems.
AIGC “Voice Cloning” Attacks
- Fraudsters gather voice samples from victims through scam call recordings.
- AI tools are used to generate synthetic audio mimicking the target’s voice.
- These audio files are used in real-time or injected attacks to exploit identity verification systems.
Fake Celebrity Advertisement Fraud Process
Fraudsters use AI to create fake celebrity advertisements, with a process that involves data collection, audio and video synthesis, advertisement distribution, and persuading victims to transfer money. This method leverages public trust in celebrities and advanced technology to enhance scam credibility.
Step 1: Data Collection
Fraudsters collect large amounts of publicly available information about a target celebrity, such as photos, videos, interviews, and social media posts. These materials are used as input for AI systems to create fake content.
Step 2: Fake Audio and Video Creation
With sufficient data, scammers use AI to synthesize audio and video. This technology allows them to replicate the celebrity’s voice and facial expressions accurately, producing fake advertisement videos. These videos are often indistinguishable from authentic ones.
Step 3: Fake Advertisement Distribution
The fake videos are distributed across various online platforms, including short video apps, social media, and group chats. These platforms often target elderly users, who are more vulnerable. Fraudsters use precise marketing techniques to reach specific demographics. Due to the realistic appearance and sound of the videos, victims are easily convinced of their authenticity.
Step 4: Building Trust and Authority
To increase success rates, scammers create a sense of urgency or use language that inspires trust. This reinforces the legitimacy of the advertisement.
Step 5: Inducing Purchases
When victims believe the content is genuine, they are directed to purchase links or customer service hotlines in the video. The products either do not exist or are substandard, resulting in financial loss for the victims.
How Ordinary People Can Identify Fake Celebrity Advertisements
Fraudsters use AI technology to create fake celebrity advertisements through a systematic process, from data collection to audio-video synthesis, advertisement distribution, and inducing victims to transfer money. These scams exploit public trust in celebrities and advanced techniques to enhance credibility. So, how can ordinary people spot fake celebrity advertisements?
-
Be skeptical of shocking or too-good-to-be-true claims, especially involving celebrities. Don’t forget common sense and logic.
-
Carefully check for unnatural features in the content, such as strange blinking patterns, mismatched audio, or distorted body parts, which may indicate deepfakes.
-
Verify the claims by cross-checking with reliable news media and websites. Don’t trust content without fact-checking it first.
-
Consult friends, family, or colleagues for advice before making decisions or purchases. Conduct in-depth research and don’t take the promoter’s word as gospel, even if it’s someone like Elon Musk.
-
Avoid commenting, sharing, or even clicking on unverified social media posts. Engaging with accounts impersonating celebrities increases the risk of being scammed.
-
Never share personal details with unverified individuals, websites, or apps.
How Platforms Can Prevent Fake Celebrity Advertisements
To address fake celebrity advertisements and information on social media platforms, the Dingxiang Business Security Intelligence Center recommends accurately identifying fake accounts as the first step in effectively preventing fraud.
-
Identifying Abnormal Devices
Dingxiang’s device fingerprinting technology records and compares device fingerprints to distinguish between legitimate users and potential fraudsters. It uniquely identifies devices and detects maliciously controlled devices, such as virtual machines, proxy servers, or emulators. The technology analyzes device behaviors, such as multi-account logins, frequent IP address changes, and alterations in device attributes that deviate from user habits, helping track and identify fraud activities. -
Identifying Abnormal Account Operations
Abnormal activities, such as logging in from different locations, device changes, phone number changes, or sudden activity in dormant accounts, require frequent verification. Continuous identity verification during sessions is essential to maintain consistency. Dingxiang’s atbCAPTCHA accurately distinguishes between humans and bots, identifies fraud in real-time, and intercepts abnormal behavior. -
Preventing Deepfake Videos
Dingxiang’s full-chain facial security threat detection solution uses multi-dimensional verification, including device environment, facial information, image authenticity, user behavior, and interaction status. It quickly identifies over 30 types of malicious attacks, such as injection attacks, fake videos, face spoofing, image forgery, camera hijacking, debugging risks, memory tampering, rooting/jailbreaking, malicious ROMs, and emulators. Upon detecting fake videos, fake face images, or abnormal interactions, the system can automatically block the operation. The solution also allows dynamic configuration of video verification intensity, balancing user experience for normal users with stricter verification for suspicious ones. -
Detecting Potential Fraud Threats
Dingxiang’s Dinsight Engine assists enterprises with risk assessment, fraud detection analysis, and real-time monitoring to improve efficiency and accuracy in risk control. Dinsight processes routine risk control strategies in under 100 milliseconds and supports multi-source data configuration and retention. It leverages mature metrics, strategies, and deep learning to enable performance monitoring and self-iteration for risk control. Combined with Xintell, its intelligent modeling platform, it optimizes security strategies for known risks and identifies potential risks through log analysis and data mining. Xintell standardizes the process from data processing and feature engineering to model deployment, providing end-to-end modeling services.


