
On April 10, 2024, password management tool company LastPass disclosed through its official blog a scam involving the impersonation of its CEO, Karim Toubba, using Deepfake technology, warning the public to beware of AI-generated fraudulent calls.
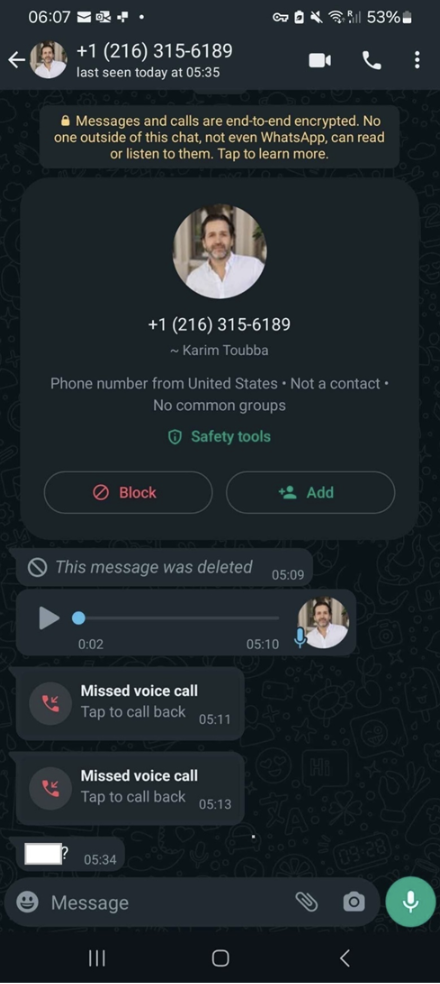
According to the blog, a fraudster impersonated LastPass CEO Karim Toubba by creating a WhatsApp account. The scammer then sent a series of messages to LastPass employees, including AI-generated voice messages imitating Karim Toubba's voice, multiple unanswered audio calls, and other communications. This created a sense of urgency to force employees into believing it was a genuine call from CEO Karim Toubba. Social engineering tactics in cybercrime often rely on creating urgency or panic to compel victims into hasty decisions.
However, the employee quickly identified this as a fraudulent call. WhatsApp is not a commonly used communication tool within LastPass, and the content of the voice messages exceeded the employee's expectations of normalcy. The employee promptly reported the incident to LastPass' security department. Subsequently, LastPass issued a notice confirming the attack did not compromise its overall security posture.
This attempted fraud highlights how advancements in AI technology, specifically voice cloning, are making cybercrime scams increasingly sophisticated. Furthermore, it underscores the importance of employee awareness training in mitigating such attacks.
These incidents continue to demonstrate the evolving complexity of cyberattacks. On the other hand, LastPass emphasizes the importance of employee awareness training in mitigating such attacks. Social engineering strategies often rely on creating urgency or panic to compel victims into hasty decisions.
AI voice cloning can generate synthetic voices for individuals with speech impairments, but it also serves as a tool for malicious actors seeking to profit from deception. To defend against AI voice cloning fraud, the Dingxiang Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center recommends several defensive measures:
-
Multi-dimensional Voice Collection: Enhance voice capture with additional dimensions. Hardware used for audio recording can include built-in sensors to detect and measure biological signals such as heartbeat, lung movements, vocal cord vibrations, and movements of the lips, jaw, and tongue. Recorded voices can be augmented with this information, providing verifiable details to distinguish natural recordings from AI fabrications.
-
Embedded Indelible Watermarks in AI Voice Fusion Tools: AI voice synthesis tools should incorporate indelible voice watermarks, such as subtle disturbances, random noise, or fixed background rhythms. These enable listeners to identify discrepancies.
-
Establishment of "Safety Words": Pre-establish a "safety word" known to family, friends, colleagues, and partners. If receiving a suspicious call, request the caller to provide this "safety word." Failure to do so can promptly identify fraudulent calls and prevent panic.
-
Hang Up and Redial: If receiving a suspicious call, simulate poor signal and promptly hang up. Then redial the purported caller's number to confirm authenticity.
In conclusion, when confronted with AI voice cloning fraud, maintaining composure and vigilance is crucial alongside implementing effective prevention and response measures. Timely reporting and cooperation with law enforcement are essential in combating such criminal activities.


