
Li's QQ account was added to a work group by a scammer. Seeing that the names in the group were those of his company's staff, he did not verify further. Days later, Li received a group message: the scammer, pretending to be the "general manager," claimed that a payment to a contractor was needed and asked Li to check the company's account balance. After verifying the funds, the "general manager" asked Li to transfer all the money to a specified account, urging him to hurry due to the urgency. Fearing to offend the "leader," Li transferred 400,000 yuan from the company account. It was only after the real general manager received a bank notification that Li realized he had been scammed.

Recently, the Ministry of Public Security announced the top ten types of telecom network fraud, with "impersonating leaders and acquaintances" standing out. Scammers use photos and names of victims' leaders or acquaintances to create fake social media accounts, add victims as friends, or include them in chat groups. They then impersonate leaders or acquaintances to gain trust by showing concern and giving commands in a familiar tone. Claiming to have transferred funds to the victim’s account and asking for a re-transfer to another account, they also send fake screenshots of successful transfers. Trusting the "leader" or "acquaintance," victims often do not verify the identity and believe the funds were transferred to their account. The scammers then push for a quick re-transfer, thus defrauding the victims. This type of fraud exploits the victim’s trust in familiar individuals, neglecting identity verification.
Criminals Using AI to Impersonate Leaders
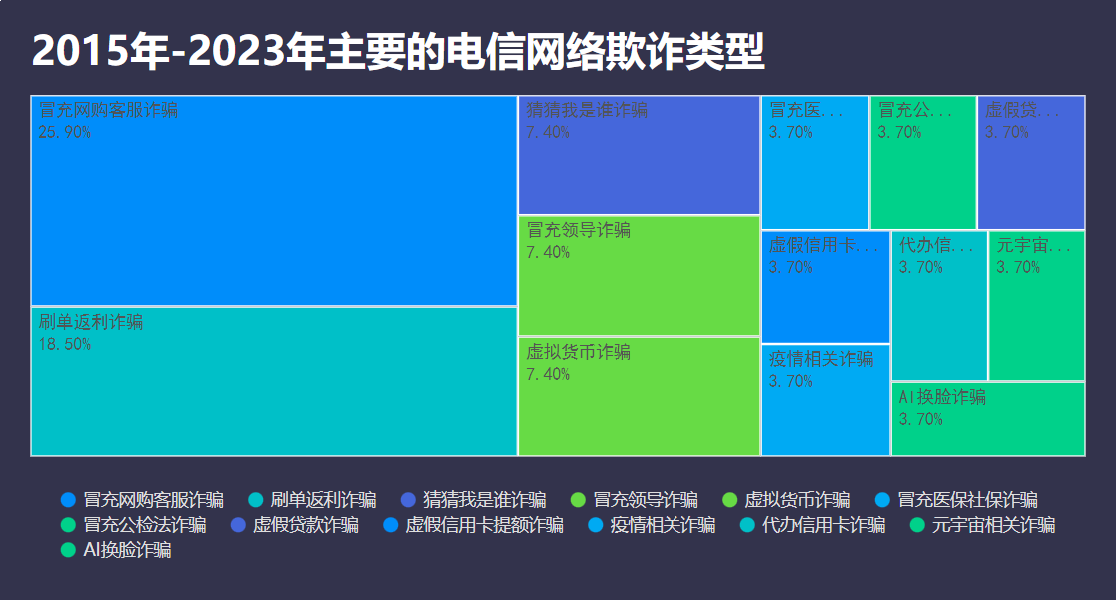
Analysis by Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center shows that from 2015 to 2023, impersonating online shopping customer service and rebate fraud were the most common types of telecom network fraud, accounting for 25.90% and 18.50%, respectively. Additionally, "impersonating leaders," "guess who I am," and cryptocurrency fraud also represented a significant proportion.
With the advancement of AI technology, high-tech fraud methods like voice cloning have become rampant. "Impersonating leaders and acquaintances" frauds have become more deceptive. Criminals use voice cloning technology and AI algorithms to mimic specific individuals' voices, creating realistic audio that sounds like genuine conversations. This technology typically employs text-to-speech conversion, turning written text into voice output. Scammers combine synthesized voices and fake video calls to further enhance the credibility of their scams. These new telecom fraud methods are more concealed and challenging to prevent.
Four Steps of AI Voice Cloning Fraud
Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center's analysis reveals the four stages scammers use to conduct voice cloning fraud. Each stage is a meticulously designed trap, and if victims cannot effectively discern, they may fall step by step into the scammers' trap.
Stage One: Information Gathering
The first step in fraud is gathering personal information about the target. Scammers obtain sensitive information like facial photos, phone numbers, and bank card numbers through black market transactions, illegal database leaks, or organized cyber attacks. This information forms the basis for the scammers' next actions.
Stage Two: Voice Synthesis
With personal information in hand, scammers use advanced voice synthesis technology and deep learning algorithms to create realistic voice samples. These samples not only mimic the target's tone and inflection but also replicate their language habits and expressions, making the voice sound indistinguishable from the real person and greatly enhancing the deception.
Stage Three: Identity Masquerade and Communication
Once the voice samples are ready, criminals start contacting the victim. They impersonate the target’s tone and style, communicating through text, voice, or video. During this stage, scammers strive to emulate the target’s everyday communication style to lower the victim’s guard and build trust.
Stage Four: Inducing Money Transfer
When the victim is convinced of the scammer's identity, the criminals begin issuing commands to transfer money or make payments. They may fabricate urgent situations or business needs, prompting the victim to transfer funds to designated bank accounts. Driven by urgency and trust, victims often comply without further verification, following the scammers’ instructions to transfer the funds.
How to Prevent "Impersonating Leaders" Scams?
Personal Precautions
When you receive a friend request on social media from someone claiming to be your leader, always verify their identity first. Avoid trusting blindly and handle friend requests cautiously. For any requests involving loans or money transfers, especially those that seem urgent or unusual, be vigilant and confirm with the leader in person through reliable channels. Only proceed with financial transactions after thoroughly verifying the situation.
Additionally, do not disclose your personal information to unfamiliar individuals online to enhance your personal prevention awareness. If you find yourself a victim of fraud, immediately preserve all related evidence and call 110 to report to the police so they can intervene promptly.
Technical Precautions
Platforms should analyze user behavior patterns and identity information to establish a security alert mechanism, monitoring and restricting suspicious activities such as abnormal logins and high-frequency messaging. By analyzing mouse movement patterns, typing styles, and other user behavior patterns, anomalies can be identified, and activities deviating from normal usage can be flagged as suspicious. Additional identity and device verification measures should be implemented, and large models can quickly screen vast amounts of data to detect subtle inconsistencies usually undetectable by humans, identifying attackers' abnormal operations.
Dingxiang Device Fingerprinting can generate a unified and unique Device Fingerprint for each device, identifying risk devices such as virtual machines, proxy servers, and emulators being maliciously controlled. It analyzes whether the device has multiple account logins, frequently changes IP addresses, or frequently changes device properties, identifying behaviors that are abnormal or inconsistent with user habits, tracking and identifying fraudsters' activities.
Dingxiang atbCAPTCHA based on AIGC technology can prevent brute force attacks, automated attacks, and phishing attacks by AI, effectively preventing unauthorized access, account hijacking, and malicious operations, thereby protecting system stability.
Dingxiang Dinsight Real-Time Risk Control Engine helps enterprises conduct risk assessments, anti-fraud analysis, and real-time monitoring, improving the efficiency and accuracy of risk control. Paired with Dinsight, the Xintell Smart Model Platform can automatically optimize security strategies for known risks, mine potential risks based on risk control logs and data, and configure different scene-supported risk control strategies with one click.


