
During the peak summer travel season, free tickets to popular museums such as the National Museum of China and the Palace Museum have become a resource out of reach for many tourists, as scalpers use illegal means to hoard these tickets and resell them at high prices.
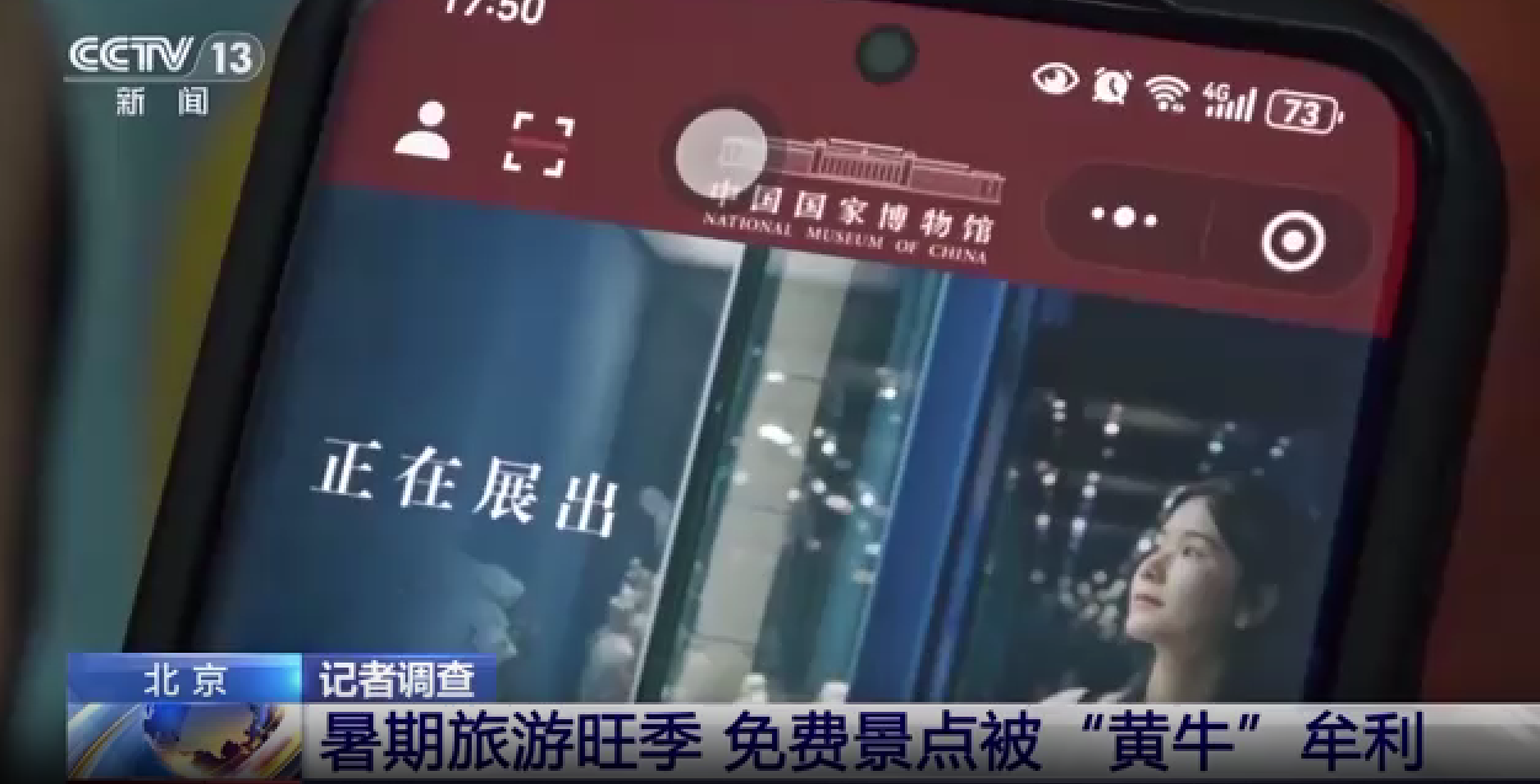 According to China Central Television, in early August, reporters repeatedly tried to book tickets through the National Museum's mini-program but found that all reservations within the week were fully booked, making it impossible to visit the museum. However, large numbers of tourists were still able to enter these popular attractions each day. Where did their tickets come from? In a random interview with 30 tourists outside the National Museum, it was found that only 2 had successfully booked tickets through official channels, while the remaining 28 obtained their tickets through scalpers at inflated prices.
According to China Central Television, in early August, reporters repeatedly tried to book tickets through the National Museum's mini-program but found that all reservations within the week were fully booked, making it impossible to visit the museum. However, large numbers of tourists were still able to enter these popular attractions each day. Where did their tickets come from? In a random interview with 30 tourists outside the National Museum, it was found that only 2 had successfully booked tickets through official channels, while the remaining 28 obtained their tickets through scalpers at inflated prices.
Reporters then searched for the "National Museum" on several online platforms and found that most discussions were related to ticketing. Scalping was prevalent on many platforms, with some even offering "guided tour" services as a cover for ticket reselling. These services were simply a front; the real purpose was to use technical means to hoard tickets and resell them at high prices.
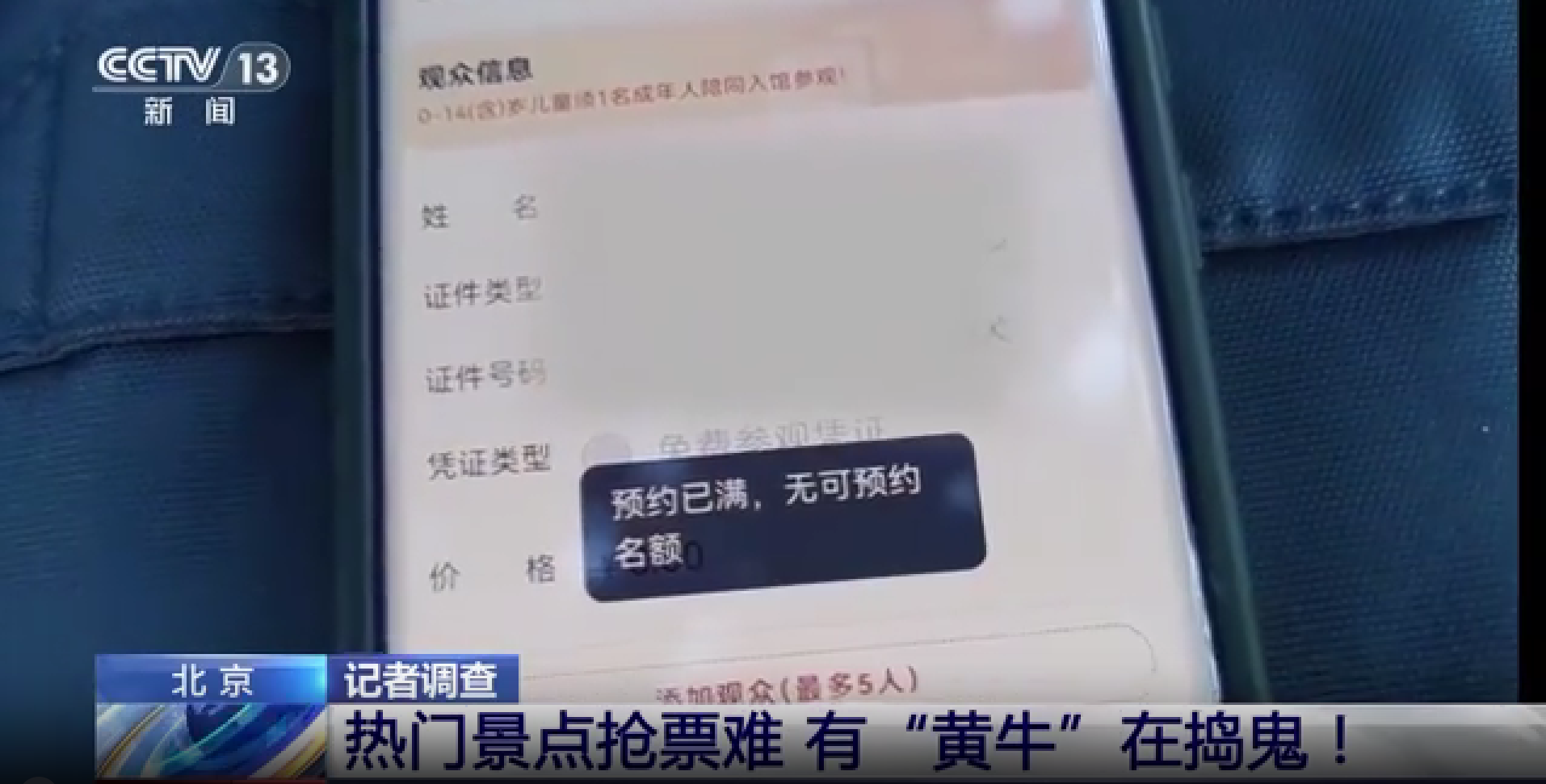
Statistics show that not only the National Museum, but also the Palace Museum, Military Museum, and other popular museums, as well as prestigious universities like Peking University and Tsinghua University, have seen this phenomenon.
The Haidian District People's Procuratorate in Beijing handled a scalping case that revealed the underlying tactics. In the case, three individuals—Li, Wang, and Zhang—used ticket-snatching software to secure reservation tickets for well-known tourist attractions nationwide, then resold them at a markup of 80 to 150 yuan. In less than a month during the 2023 summer vacation, they made over 300,000 yuan in illegal profits.
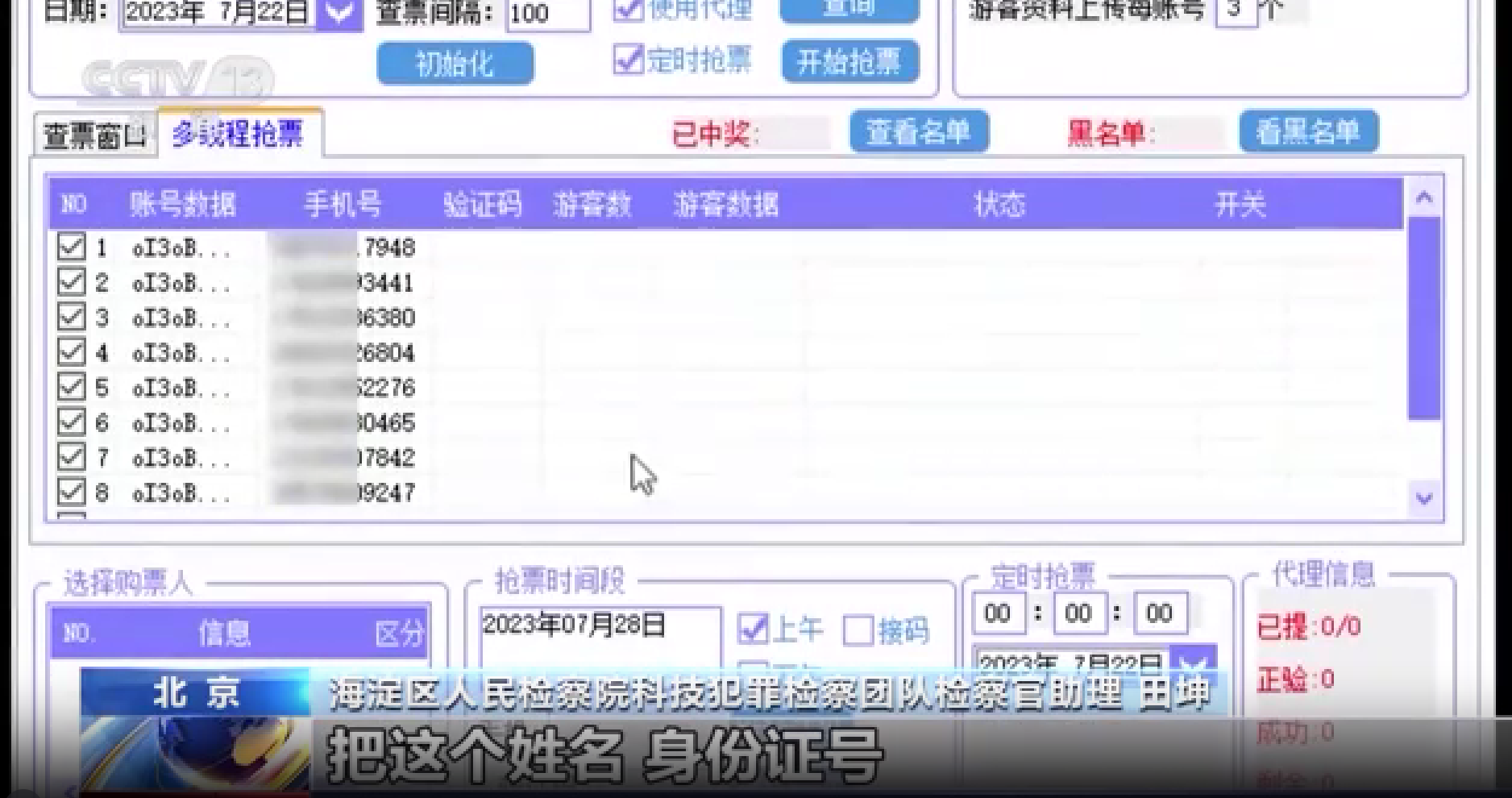
It was found that the suspects preloaded tourists' names, ID numbers, and other information into the software and used the built-in SMS code platform to receive verification codes in advance. While normal reservations required tourists to enter this information, taking up valuable time, the suspects could receive the codes two minutes earlier, with a validity of up to ten minutes, significantly increasing their chances of securing tickets. Once tickets were released by officials, these scalpers could lock in a large number of tickets within seconds with just one click.
An In-Depth Investigation into Museum Ticket Scalping
In July 2023, the 19th issue of "Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence" investigated why tourists were unable to secure museum tickets during the summer vacation. The investigation found that dozens of popular museums nationwide, including the National Museum of China, Nanjing Museum, Hunan Provincial Museum, and Shaanxi History Museum, particularly the trendy ones, had been almost entirely infiltrated by ticket scalpers.
Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center tracked and analyzed that scalpers resell free tickets mainly through three methods: real-name reservation with a surcharge, resale of tickets at higher prices, and selling guided tour packages. The first and third methods were the most common.
First Method: Reservation with a Surcharge
This requires the buyer to provide their real name, ID number, and other personal information. Ticket prices vary depending on the date, with weekdays being relatively cheaper and weekends or holidays more expensive.
Second Method: Resale of Tickets at Higher Prices
Scalpers holding multiple ID cards book tickets under one person’s name and have another person (the tourist) use that ID to enter, repeating the process.
Third Method: Selling Unauthorized Tour Packages
Some travel agency employees and private guides collaborate to register multiple museum accounts using different phone numbers, reserving tickets for various tourists and charging a service fee ranging from 10 to several tens of yuan per ticket. There are also "electronic guide + ticket reservation" or "ticket package" services, with packages including tickets, guide fees, and travel expenses.
The scalping phenomenon not only affects tourists' visiting experiences but also undermines the fairness of public resources. In these cases, relying solely on the management measures of museums or attractions is far from sufficient. A comprehensive approach involving legal, technical, and market measures is needed to improve regulatory effectiveness and curb the spread of scalping.
Why Scalpers Can Secure Tickets
Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center found that scalpers often use cheating tools like plug-in software and script programs to snatch tickets.
Ticket grabbing is a race against time. If person A is 1 second faster than person B, person A will be able to purchase the ticket, while person B will miss out. When it comes to placing orders, humans rely on nerve responses, while software operates based on preset processes. Therefore, the running speed of the software far exceeds that of humans, and the success rate of scalping is much higher than that of ordinary tourists.
Although many museums try to regulate scalpers through ticketing rules and technical means—such as blocking frequent reservations based on phone numbers and IP addresses—scalpers continuously update their cheating tools. These scalper-developed ticket-snatching tools can register, log in, and grab tickets in bulk, allowing them to quickly and instantly hoard a large number of tickets. They only need to fill in the identity information, set the quantity, and configure the running time to complete the automatic purchase.
Preventing Scalpers from Using Software to Snatch Tickets
To prevent scalpers from snatching tickets, simply restricting IPs is of little significance and may accidentally block legitimate tourist reservations. Dingxiang Defense Cloud Business Security Intelligence Center suggests that in addition to restricting IPs and accounts, technical measures should be enhanced to prevent scalpers' cheating software, thereby effectively curbing scalping.
Ticketing Rules Restrictions
-
Increase Document Usage Limits: Each ID number can only be used to make one reservation; each account can reserve tickets for up to 5 people.
-
Increase Account Usage Limits: Some museums require that if an account frequently makes reservations within a week and the no-show rate exceeds 50%, the account (phone number) will be restricted from making reservations for 30 days. Some museums also require that accounts that cancel reservations 3 times within 7 days or 5 times within 30 days, or do not enter the venue after booking, will be placed in a "blacklist" for 30 days, prohibiting further reservations, to prevent scalpers from repeatedly using identity information.
-
Increase Ticket Release Times and Channels: Releasing tickets irregularly and increasing manual random ticket releases can also reduce the chance of technical ticket snatching to some extent.
Technical Measures to Prevent Scalping
- Detect and Identify Abnormal Ticket Snatching Devices: Identify whether the client's Device Fingerprinting is legitimate and whether there are risks such as injection, hooks, or emulators. Identify whether the client's Device Fingerprinting is legitimate, quickly identify risks like flashing or modifying devices, rooting, jailbreaking, hijacking injections, etc. Quickly detect multiple activations from the same device, abnormal behavior from the same device associated with an IP, a large number of gatherings from the same IP in a short time, an abnormal proportion of old device models in the same channel, and an abnormal proportion of old operating systems in the same channel.
Dingxiang Device Fingerprinting can identify devices under malicious control such as virtual machines, proxy servers, and emulators, analyze whether the device exhibits abnormal or non-user-friendly behavior like multi-account logins, frequent IP address changes, and frequent changes in device attributes, helping to track and identify fraudulent activities. This allows for early detection of fraudulent behavior, preventing ticket snatching incidents. It can also serve as an additional factor in identity verification, enhancing security during user logins and transactions. By recording and comparing Device Fingerprinting, legitimate users can be distinguished from potential fraudulent activities.
- Detect and Block Abnormal Ticket Snatching Accounts: Use behavior-based strategies to control accounts that switch between multiple accounts on the same device to place orders.
Dingxiang atbCAPTCHA can verify, judge, and block malicious accounts and malicious scraping behaviors in real time at key stages such as registration, login, and query. It is based on AIGC technology and can prevent threats like AI brute force cracking, automated attacks, and phishing attacks, effectively preventing unauthorized access and intercepting web crawlers from stealing data. It integrates 13 verification methods and various defense strategies, supporting seamless security for legitimate users, with real-time response capabilities reduced to within 60 seconds, further improving the convenience and efficiency of the login service experience.
- Enhance Risk Identification and Prevention Capabilities: Establish a dynamic local list management mechanism based on registration data, login data, and activation data, and maintain corresponding black and white list data, including user IDs, phone numbers, devices, etc. After accumulating a certain amount of online data, use risk control data and business sediment data to model registration, login, order, and snatching behaviors, with the model output directly used in risk control strategies.
Dingxiang Dinsight Real-Time Risk Control Engine helps companies with risk assessment, anti-fraud analysis, and real-time monitoring, improving the efficiency and accuracy of risk control. The Xintell Intelligent Model Platform paired with Dinsight can automatically optimize security strategies for known risks, identify potential risks based on risk control logs and data mining, and configure risk control strategies for different scenarios with one click.


